The CND Nomenclature Rev.0
The CND nomenclature – Background and general principles
Disclaimer: This document is an interactive version of the original MDCG document. We will keep it up-to-date.
This document has been endorsed by the Medical Device Coordination Group (MDCG) established by Article 103 of Regulation (EU) 2017/745. The MDCG is composed of representatives of all Member States and it is chaired by a representative of the European Commission.
Table of Contents
The purpose of this document is to provide information regarding the basic principles and the structure of the Italian “Classificazione Nazionale Dispositivi medici” (CND). In March 2019, and according to the criteria set out by the Medical Device Coordination Group (1) (MDCG), the CND was selected as the basis for the future European Medical Device Nomenclature (EMDN). The EMDN will support the functioning of EUDAMED as stated by the MDCG and in accordance with Articles 23 of Regulation (EU) 2017/745 – MDR and Regulation (EU) 2017/746.
1. Background and General Principles
(2)
In 2005, the Italian Ministry of Health set out that the CND would be the official Italian medical device classification and nomenclature. Since then, the CND has been implemented not only in Italy, but also in Portugal and Greece.
About 15.000 manufacturers (3) from various countries have used the CND for the registration of medical devices and in vitro diagnostic medical devices in the Italian database. The distribution of manufacturers of medical devices and in vitro diagnostic medical devices per country is reported below in Figure 1.
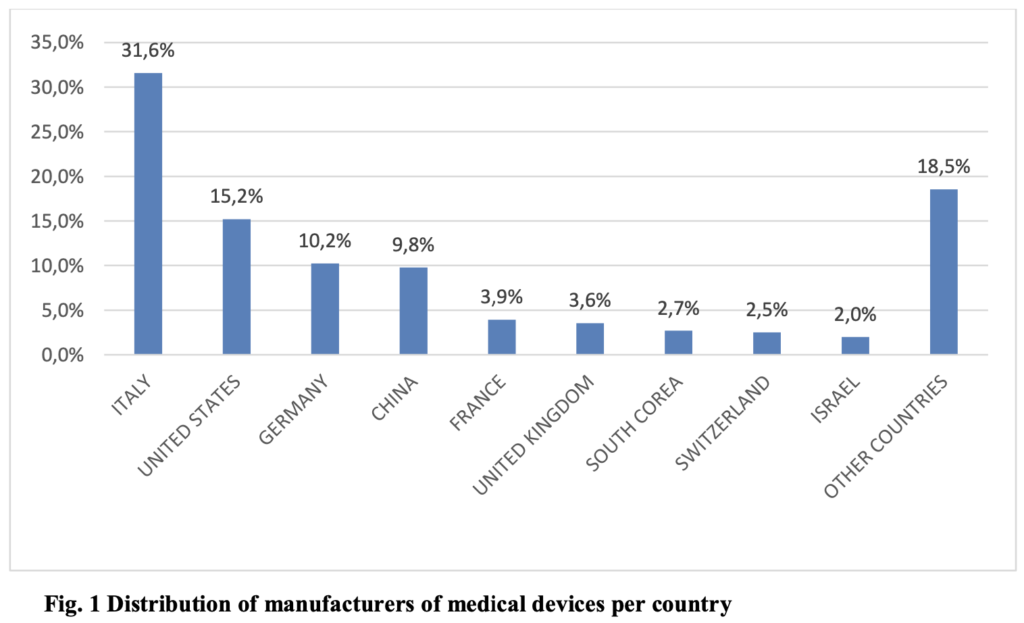
The CND nomenclature is one of the tools used in the governance of the medical device sector and is characterised by its refined and hierarchical structure. It aims to support the improvement of patient safety and the quality of health systems by enabling information to be communicated in a standardised manner.
Updates and maintenance of CND:
The construction of the CND, its subsequent updates and maintenance have been based on three fundamental principles.
A) Participative approach:
For the update and maintenance of a qualitative nomenclature, highly differentiated and qualified expertise is required. As the medical device sector is acknowledged for its heterogeneity and complexity, a broad participation of all stakeholders (economic operators and healthcare professional from NHS – at all levels of its organisation) is essential.
B) Qualified validation of proposals:
Nomenclature and Classification proposals are technically validated based on assessments of actual need. Factors taken into consideration are:
• other existing nomenclature and classification systems available at international level
• consumption and expense information
• assessment with sector experts from the different disciplines
C) Formal adoption and free public availability:
The CND system, which represents the basis of the whole information system on medical devices is formally approved and thus constitutes an official reference, freely available to all stakeholders.
More information on previous updates of the CND up to 2018 can be found in Annex I of this document.
The following products are currently not included in the CND:
- Medicinal products
- Cosmetics products
- Human blood and its derivatives;
- Organs, tissues and cells of human origin, products including human tissues and cells and products derived therefrom.
- Organs, tissues and cells of animal origin except medical devices manufactured using animal devitalized tissues or devitalized products derived from animal tissue.
- Individual Protection Devices
2. The CND structure
The CND is characterised by its alphanumeric structure that is established in a multi-level hierarchical tree. It clusters medical devices in three main levels:
- Category: the first hierarchical level
- Group: the second hierarchical level
- Type: the third hierarchical level (which if necessary, expands into several levels of detail (1°, 2°, 3°, 4° e 5°))
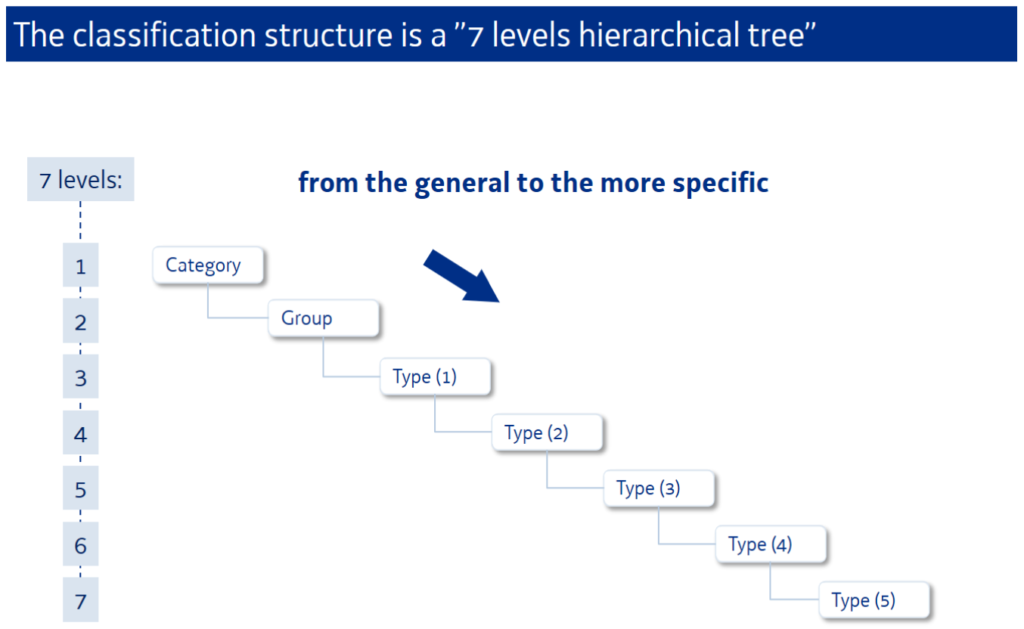
Each medical device is classified by an alphanumeric code consisting of a letter referring to the “Category”, a couple of numbers referring to the “Group” and a series of other couples of numbers referring to the “Type” (whose amount depends on the level of detail) up to a maximum of 7 levels.

Categories: the first hierarchical level
The first hierarchical level of the CND is defined as a “Category”. There are 22 categories, each identified by a letter of the alphabet:
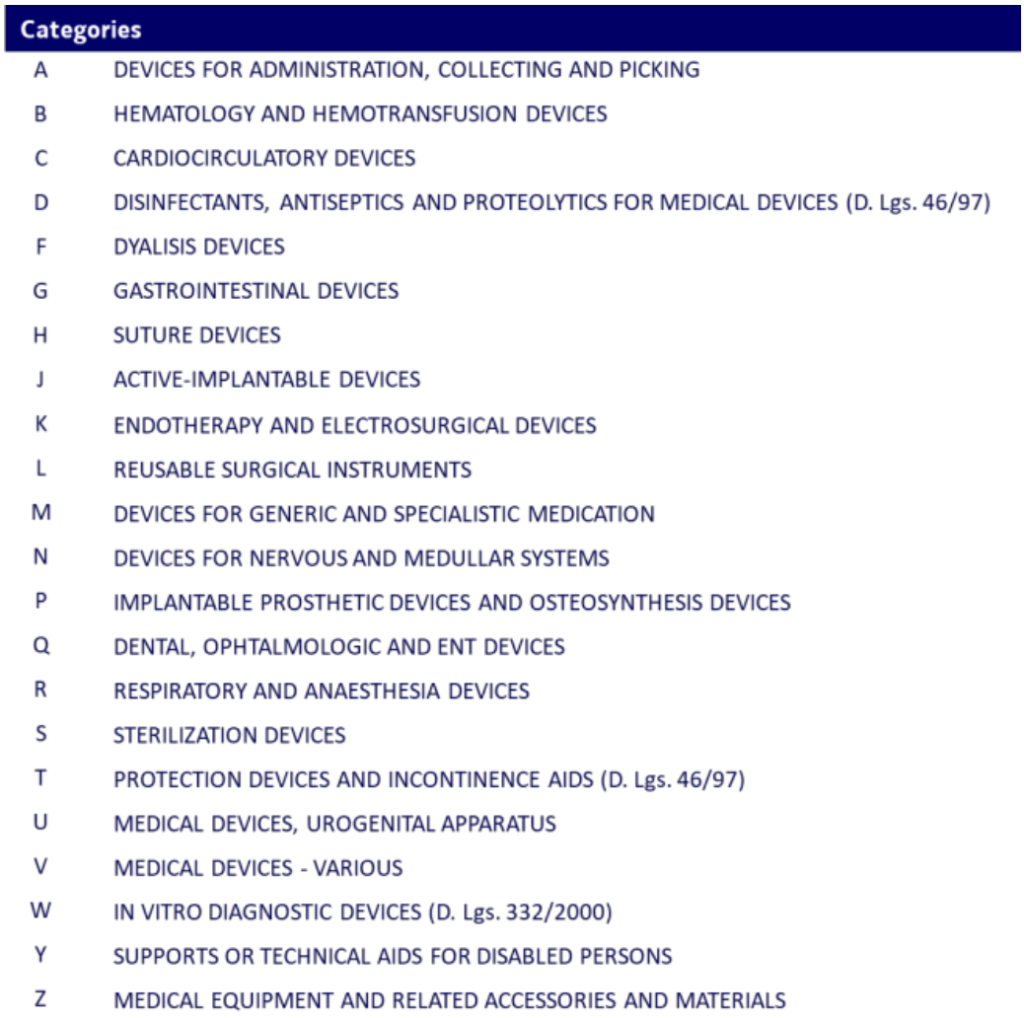
Each “Category” includes devices regulated under Directive 93/42/EEC, 90/385/EEC or 98/79/EC or following a dedicated prescription from reimbursement rules in Italy. These “categories” are used for the same specific apparatus, anatomical district or organ or as a replacement of them (anatomical categories), or devices characterised by similar use, intended use or clinical method (functional categories).
Considering these criteria and the ramified tree structure with different detail level, the following Anatomic (8), Functional (9) and Special (5) Categories have been defined:
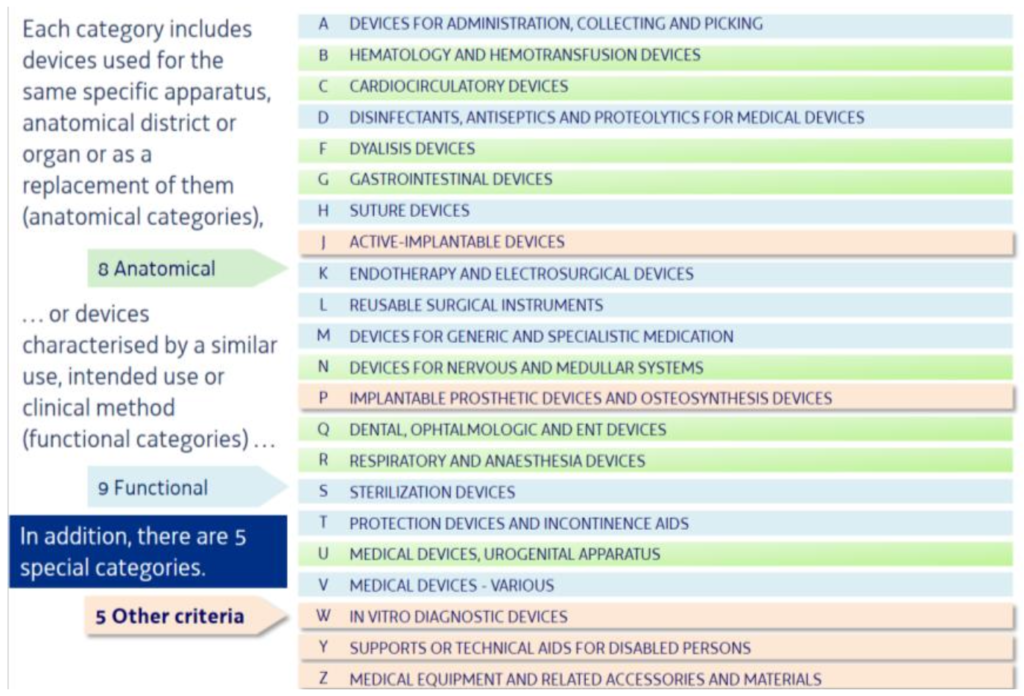
Anatomic Categories – by anatomical area of use:
- B – HEMATOLOGY AND HEMOTRANSFUSION DEVICES
- C – CARDIOCIRCULATORY DEVICES
- F – DYALISIS DEVICES
- G – GASTROINTESTINAL DEVICES
- N – DEVICES FOR NERVOUS AND MEDULLAR SYSTEMS
- Q – DENTAL, OPHTALMOLOGIC AND ENT DEVICES
- R – RESPIRATORY SISTEM AND ANAESTHESIA DEVICES
- U –UROGENITAL APPARATUS DEVICES
Functional Categories – by intended use or clinical method:
- A – DEVICES FOR ADMINISTRATION, COLLECTING AND PICKING
- D – DISINFECTANTS, ANTISEPTICS AND PROTEOLYTICS FOR MEDICAL DEVICES (regulated by Italian Legislative Decree No. 46/97 and European Directive 93/42/EEC)
- H – SUTURE DEVICES
- K – ENDOTHERAPY AND ELECTROSURGICAL DEVICES
- L – REUSABLE SURGICAL INSTRUMENTS
- M – DEVICES FOR GENERIC AND SPECIALISTIC MEDICATION
- S – STERILIZATION DEVICES
- T – PROTECTION DEVICES AND INCONTINENCE AIDS (regulated by Italian Legislative Decree No. 46/97 and European Directive 93/42/EEC)
- V – MEDICAL DEVICES – VARIOUS
Special Categories – by other criteria:
- J – ACTIVE-IMPLANTABLE DEVICES: MDs regulated by Directive 385/90 EEC
- P – IMPLANTABLE PROSTHETIC DEVICES AND OSTEOSYNTHESIS DEVICES: non-active implantable MDs
- Y – SUPPORTS OR TECHNICAL AIDS FOR DISABLED PERSONS
- W – IN VITRO DIAGNOSTIC DEVICES MDs regulated by Directive 98/79 EEC
- Z – MEDICAL EQUIPMENT AND RELATED ACCESSORIES AND MATERIALS
Groups: the second hierarchical level
The second hierarchical levels are called “Groups”. There are 146 anatomical/functional Medical Devices Groups (4), which represent the various differentiations that distinguish devices contained in the Categories. They are identified by two-digit numbers from 01 to 99 for each Category.
Number “90” identifies the groups of devices having various characteristics that are not related to existing groups. Number “99” “Altri – Others” is reserved to medical devices that are not included in already existing Groups and will be categorised in later updates.
Type: the third hierarchical level (expands into several levels of detail (1°, 2°, 3°, 4° and 5°))
The “Type” represents the third hierarchical level. If necessary, it expands into several levels of detail (1°, 2°, 3°, 4° and 5°). The group of every type includes medical devices characterised by a high affinity of use, intended use or similar clinical method. In case of doubt, the peculiar characteristics of the medical device under examination should be considered for a proper collocation or search process (i.e. the anatomic-functional characteristics and/or the intended use declared by the manufacturer).
As explained, the term “others” marked with the code “99”on the first detail level is suitable for devices not included in existing types. The “99” types will be submitted for later updates. The code reserved to the generic term “others” must be used by users only if it is not possible to classify the medical device in existing typologies. This type is subject to continuous checks and monitoring.
Regarding accessories, every accessory follows the CND classification code of the medical device that it is associated with, according to the intended use given by the manufacturer. If an accessory can be used with multiple medical devices belonging to several groups, it must be placed in the prevalent type.
3. External links
For more information, please consult the Italian Ministry website at:
The following documents may also be of use:
- National Classification of Medical Devices (CND) – as modified by Ministerial Decree 13.03.2018 (PDF format)
- National Classification of Medical Devices (CND) – as modified by Ministerial Decree 13.03.2018 (XLSX format)
- English translation of National Classification of Medical Devices Codes (as modified by Ministerial Decree 13.03.2018 -pdf, format).
- English translation of National Classification of Medical Devices Codes (as modified by Ministerial Decree 13.03.2018 -XLSX format).
- Search code and description of the CND
- Search in alphabetical order
Annex I – CND updates up to 2018
The periodical updating process of the CND was schematically subdivided into four main phases:
| This phase is open to all stakeholders who submit proposals for the definition of new classifications or for the revision of existing ones. |
| The MoH MD Technical Team (MDTT) analyses the collected proposals, the existing systems and the contents of the medical devices database to identify elements useful for classification. |
| The proposal is formally evaluated in three steps: |
| Finally, the proposal is approved by formal MoH act and published on the Italian Official journal as well as the website of the Italian MoH |
Most of the inputs adopted for updating purposes are listed below:
- The analysis of the terminal typologies „90“ and „99“:
Implemented and consolidated, it originates from the analysis of information within the Italian databank and considers data from all the medical devices registered and classified in the CND terminal types with code „90“ (- various) and „99“ (- other) of specific categories or groups identified. In fact, the classification system had already foreseen ab origine that medical devices that are not placed in a specific “typology” are classified in the generic typologies indicated with the codes 90 and 99. - Manufacturer requests:
When a manufacturer is unable to classify a medical device in an appropriate way inside the CND terminal level, a specific request for the introduction of a new CND class is required, with a communication to the MoH of a rationale and the technical characteristics and / or intended use that differentiate the device from the specific terminal classes already represented in the CND. - The analysis of CND coming from vigilance system:
Market surveillance and the vigilance system are part of the institutional activities of the MOH. The lack of classificatory level can emerge in order to identify products that need particular attention for public health. - The analysis of consumption by the NHS:
The revision of the CND made through the processing of the consumption data of the Monitoring Database is based on identification of medical devices with great economic relevance or price variability. - The analysis coming from HTA Reports:
Health Technology Assessment documents are periodically published by the Ministry of Health. These reports are considered when evaluating the revision of the CND.
The following principles were considered in the revision of the CND:
- the number of levels in the CND structure can be increased up to a maximum of seven, by coherently applying the homogeneity of the classification rules and of the coding system defined for the first CND structure.
- for the definition of a new CND branch the number of manufacturers manufacturing the medical devices that will be placed in the new typology of the CND should be more than 1;
- significant characteristics of medical devices detected by NHS professionals should be evaluated
- the proposal of relocation of medical devices placed in class 90 or 99 should be consistent.
- for the definition of a new CND branch significant differences of price between similar medical devices could be considered if necessary:
- for the definition of a new CND branch an assessments related to the use of medical devices is considered (quantity and number of users in NHS);
For each update proposal of the CND, the information associated to the devices registered in the Italian database were analysed and, if necessary, the information detected by the “Consumption Monitoring Database” were processed.
Annex II – CND VERSIONS
Art. No. 57 of the Italian Law n° 289 of the 27 December 2002 stated the requirement of the establishment of a Commission on Medical Devices (CUD) as a technical advisory board to the Ministry of Health. The CUD has the task of defining and updating the repertoire of medical devices and classifying all medical devices in specific classes and sub-classes.
The CUD defined the first version of the Classificazione Nazionale dei Dispositivi Medici (CND) on July 2005 (Italian Ministerial Decree of 22 Sept .2005). In Vitro Diagnostic Medical Devices (regulated by European Directive No. 98/79 EEC and Italian Legislative Decree No. 332/2000) were not included in the first version of the Classification, although they belong to a class of Medical Devices.
The Italian Financial Law of 2006 (Law No. 266 of the year 2005, art. 1, par. 409) established that the CND has to be approved by a decree of the Minister of Health in agreement with the State-Regions Conference.
The CUD considered it appropriate to review and update the CND with the inclusion of in vitro diagnostic medical devices before proceeding with the State-Regions Conference. Therefore, on 20 February 2007, and after a revision of the classification, the Health Minister decreed the approval of the Classificazione Nazionale dei Dispositivi Medici (CND) drawn up by the CUD. The classification refers to the medical devices regulated by Italian legislative decrees N°. 507/92, N°. 46/97, N°. 332/2000 and subsequent amendments.
In 28 March2013, the Italian D.P.R. n.44, replaced the Commission on Medical Devices (CUD) with the Technical Committee section F on medical devices.
The Classification represented the first step towards the establishment of the Italian Repertoire of the Medical Devices.
According to the art. N° 2 of The Italian Financial Law No. 266, the Technical Committee section F (previously CUD), review the CND and make the necessary changes and updates. Every update is approved by a Ministerial Decree:
- Decree of the Italian Ministry of Health (13 Mar 2008) regarding Modification and update of Classificazione Nazionale dei Dispositivi Medici (CND) published in the Official Gazette – GU No. 125 of 29/05/2008. Links:
http://www.salute.gov.it/imgs/C_17_pagineAree_328_listaFile_itemName_2_file.pdf
www.salute.gov.it/imgs/C_17_pagineAree_328_listaFile_itemName_3_file.xls - Decree of the Italian Ministry of Health (12 Feb 2010) regarding Modification and update of Classificazione Nazionale dei Dispositivi Medici (CND) published in the Official Gazette – GU No.119 of 24/05/2010. Links:
http://www.salute.gov.it/imgs/C_17_pagineAree_328_listaFile_itemName_5_file.pdf
www.salute.gov.it/imgs/C_17_pagineAree_328_listaFile_itemName_7_file.xls - Decree of the Italian Ministry of Health (7 Oct 2011) regarding Modification and update of Classificazione Nazionale dei Dispositivi Medici (CND) published in the Official Gazette – GU No.259 of 7/11/2011.Links:
http://www.salute.gov.it/imgs/C_17_pagineAree_328_listaFile_itemName_9_file.pdf
www.salute.gov.it/imgs/C_17_pagineAree_328_listaFile_itemName_10_file.xls - Decree of the Italian Ministry of Health (29 July 2013) regarding Modification and update of Classificazione Nazionale dei Dispositivi Medici (CND) published in the Official Gazette – GU No. 258 of 04/11/2013). Links:
http://www.salute.gov.it/imgs/C_17_pagineAree_328_listaFile_itemName_16_file.pdf
www.salute.gov.it/imgs/C_17_pagineAree_328_listaFile_itemName_17_file.xlsx - Decree of the Italian Ministry of Health (8 June 2016) regarding Modification and update of the Classificazione Nazionale dei Dispositivi Medici (CND) published in the Official Gazette G.U. Serie Generale, n. 242 del 15/10/2016).
- Decree of the Italian Ministry of Health (13 march 2018) regarding Modification and update of the Classificazione Nazionale dei Dispositivi Medici (CND) published in the Official Gazette G.U. Serie Generale, No. 116 del 21/05/2018). Links:
http://www.salute.gov.it/imgs/C_17_pagineAree_328_listaFile_itemName_15_file.pdf
www.salute.gov.it/imgs/C_17_pagineAree_328_listaFile_itemName_18_file.xlsx
Footnotes
(1): (MDCG 2018-2) – Future EU medical device nomenclature: Description of requirements
(2): The principles and rules presented thereafter are the ones historically established/followed when building the CND nomenclature up to the last update in 2018. This is without prejudice to the new rules that will govern the EMDN which will be established by the MDCG.
(3): Source NSIS: data updated on 10 August 2019
(4): Updated as of the Italian Ministerial Decree of 13 March 2018.
